Understanding the Sudden Onset of Heartburn
Encountering the unsettling fiery discomfort within your chest, often referred to as heartburn, can be simultaneously agonizing and disconcerting. Especially when it manifests abruptly and devoid of any apparent trigger. If you’re left contemplating, “What’s causing this sudden onset of heartburn?” rest assured, you’re not alone. This all-encompassing manual will explore the typical catalysts behind the abrupt emergence of heartburn and offer strategies for mitigating it.
Demystifying Heartburn: A Comprehensive Guide
Heartburn, which is often equated with acid reflux, is not just a momentary irritation. It’s characterized by an unsettling burning sensation that courses through your chest. Contrary to what its name suggests, it has nothing to do with the heart. Instead, it’s the aftermath of stomach acid or semi-digested food making a reverse trip into the esophagus. While it’s normal for many people to occasionally experience heartburn, regular occurrences can hint at a more serious issue, like the widely-recognized gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
Tips for Recognizing:
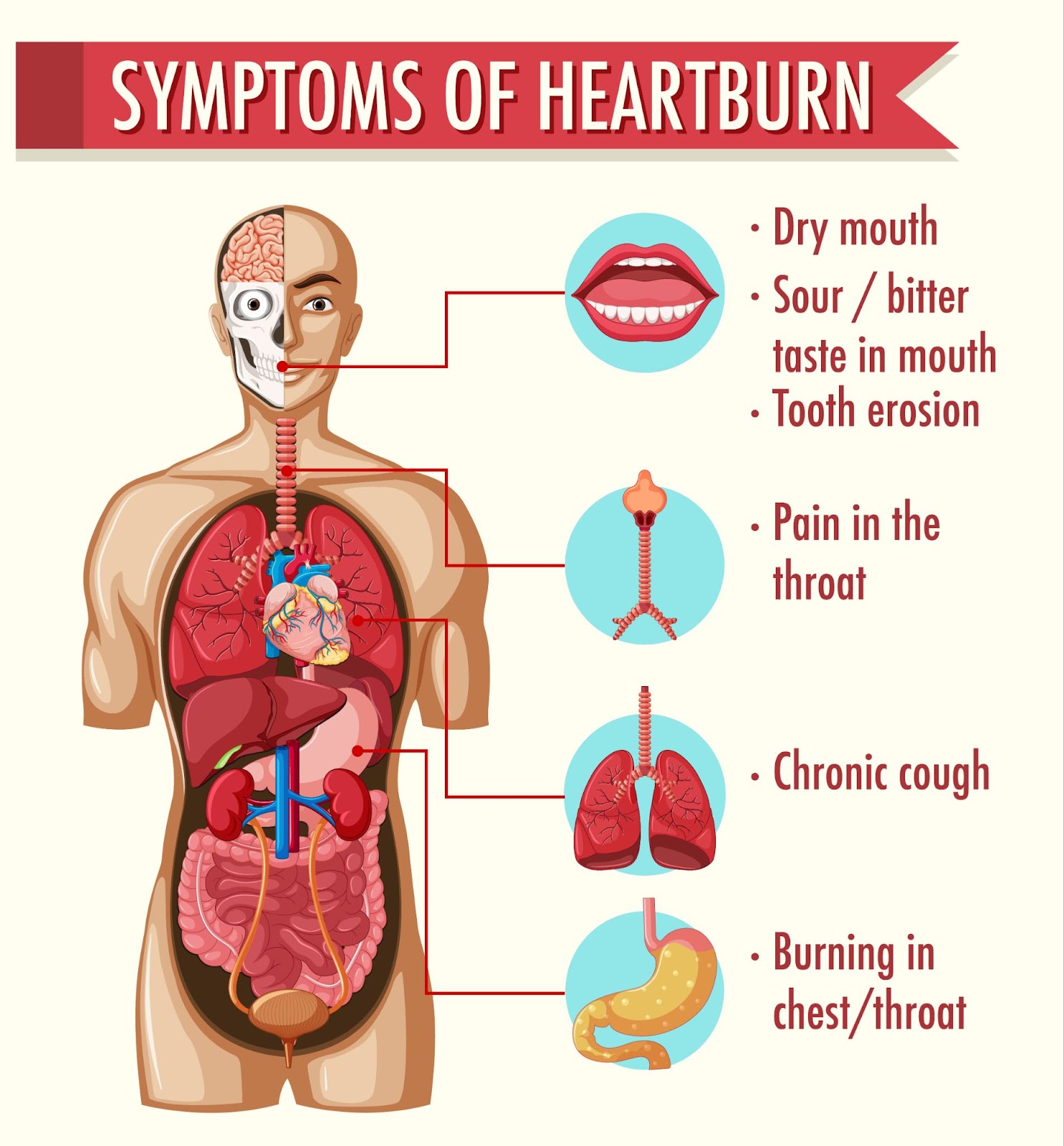
- A burning or painful sensation in the chest area, often after meals;
- A sour or bitter taste in the mouth, indicating acid backup;
- Symptoms that get worse when lying down or bending over.
Dissecting Heartburn: The Unwanted Acidic Visitor
When you delve into the intricacies of heartburn, it becomes evident that the primary culprit is the untimely ascent of stomach acid or semi-digested food into the esophagus. This can produce a scalding sensation in the chest, eerily reminiscent of heart ailments. To understand this better, let’s dive into the mechanics behind this condition:
- The Lower Esophageal Sphincter (LES) plays a pivotal role. Think of the LES as a muscular gatekeeper, situated at the meeting point of your stomach and esophagus. Its main job? To keep stomach contents, including powerful digestive acids, confined to the stomach;
- Issues arise when the LES isn’t performing at its best. If it becomes weakened or doesn’t seal properly, it inadvertently lets stomach acid and food seep into the esophagus.
Once these acidic contents come in contact with the delicate esophageal lining, they cause irritation. This discomfort manifests as the familiar burning sensation we know as heartburn.
Recommendations to Alleviate Heartburn:
- Consume smaller meals to avoid overburdening your stomach;
- Wait for at least two hours after eating before lying down;
- Elevate the head of your bed slightly to keep stomach acid at bay.
Limit foods that are known triggers, such as spicy dishes, citrus fruits, and caffeinated drinks.
Insights:
- Chronic heartburn can lead to esophagitis, an inflammation of the esophagus;
- Lifestyle changes, including diet modifications and weight loss, can significantly reduce heartburn episodes;
- Over-the-counter antacids can offer immediate relief, but it’s essential to consult a doctor if heartburn persists.
Common Causes of Sudden Heartburn
Dietary Delinquents: What You Consume Matters
Your dietary choices can either fortify or undermine the integrity of the LES. Be mindful of what you consume to keep heartburn at bay:
- Spicy Foods: The heat in spicy cuisine can also ignite heartburn. Capsaicin, the compound responsible for spiciness, can relax the LES, facilitating acid reflux;
- Acidic Foods: Foods like tomatoes and citrus fruits are notorious for their acidity, which can weaken the LES and lead to heartburn;
- Fatty or Fried Foods: High-fat meals take longer to digest, keeping the stomach active and more prone to reflux;
- Caffeine and Carbonated Beverages: These can relax the LES and increase stomach acid production, a recipe for heartburn;
- Alcohol: Booze can irritate the esophagus lining and contribute to LES relaxation, making alcohol a trigger;
- Chocolate: Though delightful to the taste buds, chocolate contains theobromine, a compound that may cause the LES to relax, inviting heartburn;
- Peppermint: While a soothing herb for many ailments, peppermint can relax the LES, potentially promoting acid reflux.
Medications and Their Hidden Effects
Surprisingly, the medications you take can also play a role in causing or worsening heartburn. Keep an eye out for these culprits:
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen can irritate the stomach lining, contributing to acid reflux;
- Blood Pressure Medications: Some drugs prescribed for hypertension management can relax the LES, leading to heartburn;
- Asthma Medicines: Certain inhalers and medications used to manage asthma can also have a side effect of relaxing the LES, increasing the risk of acid reflux;
- Antidepressants and Sedatives: These medications can interfere with the normal functioning of the LES, potentially promoting heartburn;
- Calcium Channel Blockers: Prescribed for conditions like high blood pressure, these medications can relax the LES, allowing acid to flow upward.
Lifestyle Choices: Tread Carefully
Your daily routines and habits can inadvertently open the door to heartburn. Here’s how you can make wiser choices:
- Overeating or Eating Before Bed: A full stomach can put pressure on the LES, increasing the likelihood of reflux. Avoid heavy meals close to bedtime;
- Clothing Matters: Tight-fitting clothes or belts can squeeze the abdomen, pushing stomach contents upward. Opt for looser attire;
- Smoking: Smoking not only damages the LES but also increases stomach acid production, doubling the trouble;
- Weight Matters: Being overweight or obese can increase abdominal pressure, forcing stomach acid into the esophagus.
Medical Conditions: Uninvited Guests
Several underlying medical conditions can also conspire to bring about heartburn:
- Hiatal Hernia: This condition occurs when part of the stomach pushes up through the diaphragm muscle, making acid reflux more likely;
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes and increased abdominal pressure during pregnancy can trigger heartburn in expecting mothers;
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): Chronic acid reflux, often linked to a weakened LES, characterizes this condition;
- Gastroparesis: Delayed stomach emptying, a condition often found in diabetes patients, can contribute to heartburn due to food remaining in the stomach for longer periods.
Tips for Alleviating Heartburn and Promoting Digestive Health
Now that we’ve delved into the potential complications of heartburn, let’s explore practical ways to alleviate this discomfort and maintain a healthy digestive system. Implementing these strategies can help you manage heartburn effectively:
Watch Your Diet: Choose Wisely
Identifying and controlling the culprits responsible for triggering your heartburn is essential. These usual suspects encompass spicy cuisine, citrus fruits, tomatoes, chocolate, and the indulgence of fried or high-fat foods.
Opting for a well-rounded dietary regimen, replete with fiber, an abundance of fruits and vegetables, and lean sources of protein, proves to be a wise choice.
Consider the practice of maintaining a meticulous food journal to meticulously track and decipher your particular triggers.
Embrace the strategy of consuming smaller, more frequent meals. This not only serves as a bulwark against overindulgence but also alleviates the undue pressure exerted on the lower esophageal sphincter (LES). In doing so, it orchestrates a more equitable distribution of the digestive workload throughout the course of the day.
Harness the force of gravity as a dependable ally during slumber. Elevate your head and upper body with the assistance of pillows. This uncomplicated measure effectively blocks the regurgitation of stomach acid into the esophagus, thereby curtailing nighttime heartburn.
Following your meals, uphold an upright posture for a minimum of two hours before reclining or lying down. This temporal restraint grants your digestive system the opportunity to thoroughly process food, thereby diminishing the risk of unwarranted acid reflux.
Moderation is the watchword when it comes to alcohol and caffeine consumption. Both of these substances possess the capacity to weaken the LES, rendering it more susceptible to the backwash of stomach acid into the esophagus. Thus, exercising restraint in their consumption, especially during the evening hours, is paramount.
Lose Weight: Shedding Pounds, Reducing Heartburn
- If you’re overweight or obese, losing weight can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of heartburn episodes;
- Even a modest weight loss can make a noticeable difference in your symptoms.
Quit Smoking: Breaking the Nicotine Connection
- Smoking introduces nicotine into your body, which relaxes the LES and promotes acid reflux;
- Quitting smoking not only benefits your overall health but also reduces heartburn.
Recognizing the Right Time to Consult a Doctor About Heartburn
Heartburn is a common affliction, experienced by many at some point in their lives. While occasional heartburn after a heavy meal or spicy foods might be a typical occurrence, there are times when heartburn could be a signal for a more severe underlying issue. It’s vital to recognize these red flags and understand when to seek professional medical advice.

Characteristics of Concerning Heartburn:
- Severity: If the burning sensation is extremely painful or unbearable, it shouldn’t be ignored;
- Frequency: Experiencing heartburn multiple times a week can be an indicator of a more serious condition, like gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD);
- Duration: Heartburn that persists longer than usual or doesn’t subside with over-the-counter antacids may warrant a doctor’s attention.
Why It’s Important to Consult a Doctor:
- Accurate Diagnosis: A healthcare professional can differentiate between regular heartburn and conditions like GERD, esophageal cancer, or even potential heart issues;
- Tailored Treatments: Not all heartburn is the same. A doctor can prescribe the most appropriate medication or treatment plan tailored to the individual’s needs;
- Preventing Further Complications: Chronic heartburn can lead to complications like esophageal ulcers or Barrett’s esophagus. Early detection and treatment can prevent these;
- Peace of Mind: Ruling out serious conditions, especially heart problems, can alleviate stress and anxiety.
Recommendations:
- Maintain a Heartburn Diary: Keeping track of foods, drinks, or activities that trigger heartburn can be useful when discussing symptoms with a doctor;
- Avoid Self-Diagnosis: While the internet is full of information, self-diagnosis can sometimes be misleading. Rely on professional advice for accurate conclusions;
- Opt for Regular Check-ups: Especially for those with frequent heartburn, regular check-ups can help in monitoring the condition and making necessary treatment adjustments.
In conclusion, it’s always better to err on the side of caution. If there’s any doubt about the nature or intensity of heartburn, consult a medical professional for a comprehensive understanding and the best course of action.
Conclusion
Heartburn, though quite unpleasant, ranks as a prevalent affliction. Gaining insight into the various factors that might incite it can be instrumental in diminishing both its occurrence and intensity. Whether it involves implementing alterations in one’s diet, modifying daily routines, or consulting with healthcare professionals, tending to the underlying origins of sudden heartburn can pave the way for a life that’s notably more comfortable and devoid of troublesome symptoms.